What is antimicrobial resistance?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is when microbes such as bacteria, viruses and fungi evolve mechanisms to overcome the actions of treatments designed to kill them.
When bacteria develop resistance against treatments like antibiotics we refer to this process as antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic-resistant infections hinder patient health and place significant burdens on healthcare systems. Antibiotic resistance also increases the danger of carrying out routine medical procedures such as hip replacements. This is because we may eventually lack effective therapies which can successfully treat bacterial infections which can arise from these surgeries.
Over 4.7 million deaths were associated with AMR in 2021(1).
In 2023, 1 in 6 bacterial infections were antibiotic resistant(2).
Between 2025 and 2050, it is predicted that 169 million deaths will be associated with AMR(1).
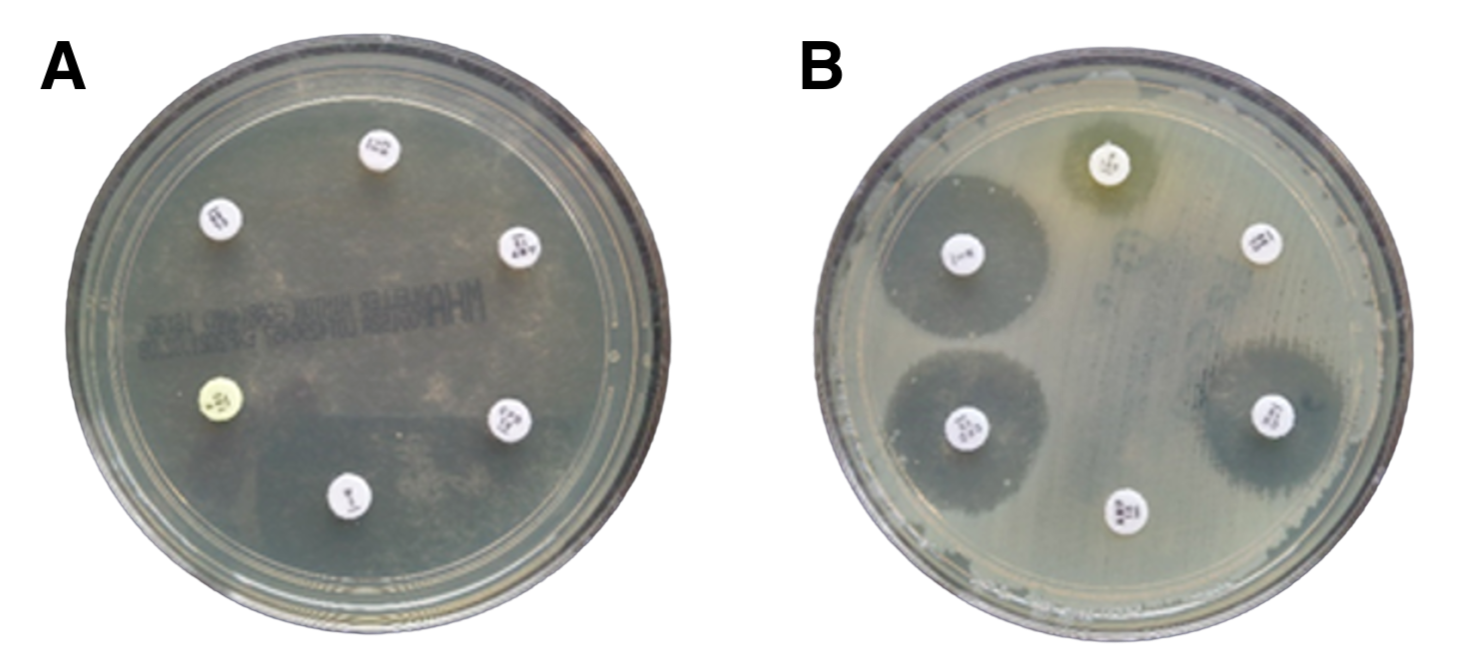
Image credit: Dr Liz Sheridan - Microbiology Department, University Hospitals Dorset
To determine bacteria’s resistance to antibiotics, scientists and clinical microbiologists grow the microorganism on an agar plate with paper disks infused with different antibiotics. This method, referred to as the Kirby-Bauer diffusion test, evaluates the bacteria’s susceptibility to each antibiotic.
Clear zones around the paper disks, known as the ‘zones of inhibition’, indicate that the bacteria is susceptible to the antibiotic.
In the image above, we have two agar plates, Plate A and Plate B. Plate A tests the antibiotic susceptibility of the bacteria Escherichia coli, responsible for causing a urinary tract infection (UTI) in Patient 1. Plate B tests a different strain of E. coli responsible for Patient 2’s chronic UTI.
Plate A illustrates that Patient 1’s UTI is susceptible to antibiotic treatment, because the agar plate is clear of bacterial growth. In contrast, Plate B shows that Patient 2 has an antibiotic-resistant infection. Compared to Plate A, Plate B shows bacterial growth (cloudy layer) and either small or no clear zones around the antibiotic-soaked paper disks. This result suggests that’s Patient 2 may require stronger antibiotics or alternative treatments to effectively clear their UTI.
AMR in England
AMR is associated with 32,500 deaths annually in the UK and estimated to cost the NHS £180 million per year(3-4)
On average there were 400 cases of antibiotic-resistant infections per week in England in 2024(5)
Since 2019, Escherichia coli has been responsible for 65% of antibiotic-resistant bloodstream infections(5)
Regionally, London experiences the greatest AMR burden(5)
Adults over 74 years of age are the most at risk of contracting a resistant infection(5)
Antibiotic resistance disproportionally effects individuals living in the most deprived areas, with rates of antibiotic-resistant bloodstream infections 47.2% higher in these settings, compared to the least deprived areas(5)
The burden of infections in the UK
Infectious diseases, particularly those resistant to antimicrobials, have been recognised by the UK Government as a major public health concern which requires urgent action. Beyond increasing costs to the NHS and negatively impacting patient health, infectious diseases also drive antimicrobial prescribing, which accelerates the rate of antimicrobial resistance.
Three infections responsible for most antibiotic prescribing in UK general practices include respiratory, urinary tract and skin and soft tissue infections.
Respiratory infections
In general practice, respiratory infections are the main infection that drive antibiotic prescribing(5)
At the end of the 2024 financial year there were over 250,000 hospital admissions for pneumonia(6)
Lower respiratory infections are the fourth largest cause of death in the UK(7)
To learn more about pneumonia, additional respiratory infections and research in this field follow the links below:
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
UTIs are the second most common infection for antibiotic prescribing after respiratory infections(5)
Over half of bloodstream infections caused by E. coli in England are a consequence of UTIs(5)
Between 2023 and 2024, UTIs were responsible for over 180,000 hospitalisations in England, accounting for 1.2 million NHS bed days and costs worth over £600 million(8)
In October, our Project Coordinator Esme spoke to Melissa Kramer from Live UTI Free about how we can utilise phage therapy to treat UTIs. To learn more about this, you can watch the video here.
Skin and soft tissue infections
Wound care is estimated to cost the NHS £8.3 billion per year(9)
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a species of bacteria responsible for driving skin infections, has been acknowledged by the World Health Organization as a ‘High’ bacterial priority pathogen(10)
Rates of resistance in S. aureus increased by 33% between 2019 and 2024 in England(5)
To learn more about skin and soft tissue infections follow the links below:
Alternative antimicrobials
Phages, viruses which infect and kill bacteria, may offer a promising alternative antimicrobial therapy to treat antibiotic-resistant infections. These tiny entities are the most abundant biological entity on this planet and can be found in any environment where bacteria reside such as rivers, soil and the human gut.
Want to learn more about phages? Check out our page ‘What are phages?’
Scientists apply these bacterial viruses in therapies to target and kill the specific bacterial strain(s) responsible for causing a patient’s infection. For example, Patient B (see above) is suffering from a chronic UTI caused by an E. coli strain which is resistant to antibiotics. Scientists isolate phages against the patients E. coli strain and formulate a phage cocktail, consisting of multiple different phages which can effectively infect and kill the bacteria. This cocktail is manufactured into a drug product and then administered to the patient as appropriate under clinical care.
To learn more about phage therapy check out our ‘What is phage therapy?’ page
With support from citizen scientists, the Phage Collection Project isolates, characterises and biobanks phages from diverse samples sent across the world. We investigate the phages therapeutic potential with the aim to further phage therapy research and support clinical trials.
To learn more how you can get involved in the Phage Collection Project’s research check out our ‘What is citizen science?’ page.
References
(1) Naghavi, M. Vollset, SE. Ikuta, KS. Swetschinski, LR. Gray, AP. Wool, EE et al. Lancet 2024. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050.
(2) World Health Organization (WHO). 2025. Global antibiotic resistance surveillance report 2025: WHO Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS).
(3) House of Commons. 2025. Antimicrobial resistance: addressing the risks.
(4) House of Commons Health and Social Care Committee. 2018. Oral evidence: Antimicrobial resistance.
(5) UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA). 2025. English surveillance programme for antimicrobial utilisation and resistance (ESPAUR) Report 2024 to 2025.
(6) Office for Health Improvement & Disparities. 2025. Respiratory disease profile: statistical commentary, June 2025.
(7) World Health Organization Data. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
(8) UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA). 2025. Understanding the burden of UTI hospitalisations in England. 2025.
(9) Guest, JF. Fuller, GW. Vowden, P. BMJ Open 2020. Cohort study evaluating the burden of wounds to the UK’s National Health Service in 2017/2018: update from 2012/2013.
(10) World Health Organization (WHO). 2024. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: bacterial pathogens of public importance to guide research, development and strategies to prevent and control antimicrobial resistance.